Loading an Application for Development
The Verse Extension API is heavily influenced by the Chrome/Firefox Web Extension API. This is used to emulate deploying an application without needing to acutally deploy with Domino which streamlines development and testing.
Prerequisites
There are a few things you will need to get started:
- Google Chrome or Firefox (Version 49.0 or greater)
- Your custom application or a local copy of the Verse Developer Extension Demo source code.
- contentscript.js and page.js from here (Only if you are using your custom application)
Configuration
Some files will need to be configured and added to your application directory for successful deployment.
The Manifest
The first file you will need to configure before deploying is the manifest.json. The manifest is a uniform file, used for both Chrome and Firefox web add-ons, to specify some basic application properties such as the name, version, and URL(s) of where the extension should run. For more information take a look at the, manifest.json, Browser Compatibility Documentation.
Demo manifest.json:
The matches property contains an array of URLs that tell the browser where the extension should run; more specifically, what pages the contentscript.js file should be injected into. The field should be updated to match that of your own Verse URL. The * you see at the end of the example URLs mean matching 0 or more characters. It is recommended to add the star, otherwise, the extension will not run on pages of Verse where the URL does not match, exactly, one of the specified URLS. In addition, a comma should be added to the end of each URL, except for the last one.
note
Trailing commas in the manifest.json and applications.json can result in parsing errors, causing your application to fail to load.
The web_accessible_resources field is an array of paths and should include the applications.json and the page.js file. Other resources including images, HTML, CSS, and JavaScript can be specified in the array, making them accessible to the browser. You can read more about the web_accessible_resources property here.
The Scripts
There are two important scripts required to load the applications.json. They should be added, unaltered, to your project directory and included in the manifest.json exactly as shown in the above example. Their purpose is to mimic the initialization behavior of the WidgetRegistry, which is used to load applications in Verse.
Scripts:
content.jspage.js
Using Web Accessible Resources
For development purposes, additional application resources can be easily accessed from your web extension's web_accessible_resources by using ${extensionPath} as the base url of the path.
Before the applications.json is loaded into Verse, it is parsed and all instances of ${extensionPath} are replaced with a fully-qualified URL. For this to work correctly, any resources accessed this way must be declared in the web_accessible_resources array of the manifest.json.
Example Extension linking to Additional Resources:
caution
When deploying for production use, your resources will need to be hosted via a web server and the ${extensionPath} shortcut must be updated according otherwise, your resources will not load.
Installation
Now that the necessary files have been added and configured, you can load your extension into the browser using Chrome or Firefox.
Installing to Chrome (Latest)
- Navigate to
chrome://extensionsinside of Chrome - Make sure Developer Mode is toggled on, in the upper right corner of the browser
- Select the Load Unpacked option
- Select the root folder containing the
manifest.json(in this example it is in the/srcfolder)
Installing to Firefox (Latest)
- Navigate to
about:debuggingand select This Firefox from the left panel - Select the Load Temporary Add-on option
- Select the
manifest.jsonfile (not its containing folder)
Check it Out!
After following one of the above methods, reload Verse to test your new application.
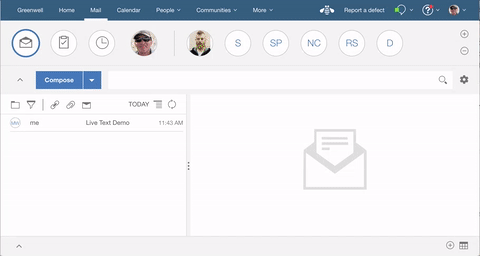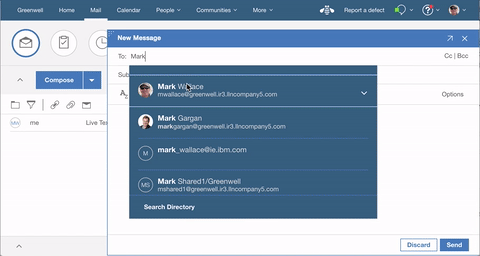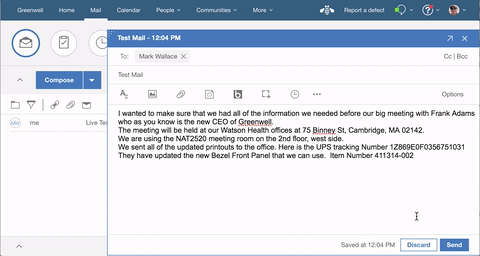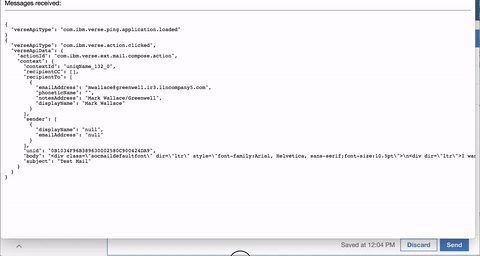
If you deployed your own custom application then look in the Verse UI for your own changes. The demo application is a Widget extension type that adds a new action to a dropdown menu in the Mail Compose View and an action to back of the Verse people business card. Clicking on the application opens the specified HTML file that is served via the local web server. This widget, also, leverages the Verse Data API to receive useful Verse information in the browser (Ex. a business card action extension sends the person’s name, email, phone, etc.).
info
To learn more about the different types of extensions that Verse has to offer head over the the Extension Documentation.